Both Active Listening and Empathy
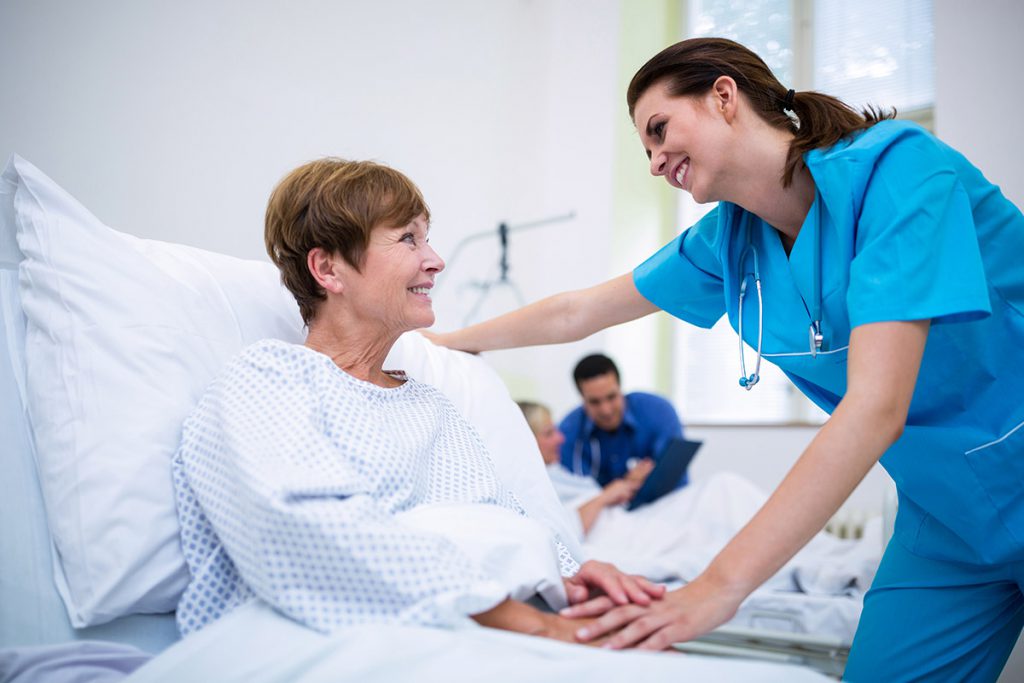
Empathy: By placing themselves in the patient’s position, medical personnel can develop empathy. Comprehending and recognizing the feelings of patients cultivates a sympathetic relationship.
Active listening is paying close attention to what a patient is saying, comprehending it, reacting to it, and keeping it in mind. It covers strategies like summarizing, paraphrasing, and posing open-ended inquiries.
Cultural Proficiency
Training in cultural competence—the ability to recognize and value differences in people’s backgrounds, customs, and communication styles—should be required of healthcare personnel.
Healthcare professionals that possess cultural competence are able to interact with patients from different cultural backgrounds in an efficient manner and earn their trust.
Simple and Unambiguous Wording
Healthcare professionals should avoid using technical terms that patients might find confusing when communicating medical information and instead use plain language.
Patients are more likely to understand their diagnoses, treatment plans, and other medical information when the language is tailored to their comprehension level.
Programs for Patient Education
Continuous patient education initiatives assist medical practitioners in explaining complicated medical concepts in a way that patients can understand.
Resources, workshops, and materials that assist medical professionals in informing patients about their conditions and available treatments may be included in these programs.
Simulation and Role-Playing:
Healthcare professionals can practice effective communication in realistic scenarios through role-playing exercises and simulations.
Healthcare professionals can improve their communication skills and build confidence in managing a range of patient interactions by receiving feedback and practicing.
Training in Conflict Resolution
Healthcare workers who receive conflict resolution training are better prepared to handle difficult patient conversations or disagreements.
Active listening, keeping a composed expression, and working together to find solutions to patients’ problems are some of the techniques.
Collaboration within a Team:
For patient care to be coordinated and seamless, healthcare teams must communicate effectively with one another.
Training places a strong emphasis on the value of prompt information exchange, effective communication, and teamwork amongst the various healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care.
Technology Use
Training is required for healthcare personnel to use communication technologies such as telemedicine platforms and Electronic Health Records (EHRs).
Being proficient with these technologies guarantees safe and effective communication, which improves patient care and information exchange.
Comments and Ongoing Development:
By creating a feedback culture, healthcare professionals can get helpful criticism on their communication abilities.
Constant improvement entails introspection, experience-based learning, and proactive pursuit of chances to improve communication efficacy.
Patient-First Healthcare
Personalized care plans and patient participation in decision-making are key components of patient-centered care.
The main focus of training is on shared decision-making, in which patients and healthcare providers work together to make decisions that are well-informed and grounded in the patient’s values and goals.
Healthcare professionals can improve patient satisfaction, improve health outcomes, and adopt a more patient-centered approach to care by implementing these strategies into their daily practices and training programs.