Artificial intelligence, or AI for short, is a paradigm change in technology where machines exhibit intelligent behavior that is traditionally associated with humans. In the healthcare sector, artificial intelligence (AI) optimizes resource allocation, expedites processes, improves patient outcomes, and strengthens clinical decision-making. The complicated topic of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare will be covered in this essay, along with key concepts, applications, benefits, practical applications, and future advances. Understanding AI in Medical
The term artificial intelligence (AI) encompasses a range of technologies that enable robots to replicate human cognitive abilities in diverse domains, including data analysis, pattern recognition, decision-making, and environment interaction. Numerous healthcare applications are utilizing artificial intelligence (AI), including patient monitoring and
Healthcare Applications of AI
1. Machine Learning (ML): ML techniques enable machines to learn from data and form conclusions or predictions by utilizing patterns and insights. Examples of predictive analytics in healthcare include risk assessment, customized treatment suggestions, and patient outcomes.
2. Deep Learning (DL): DL is a branch of machine learning (ML) that uses multiple-layer neural networks to handle complex data and extract hierarchical representations. It powers clinical documentation and medical transcribing applications, including image recognition in pathology, dermatology, and radiology, as well as natural language processing (NLP).
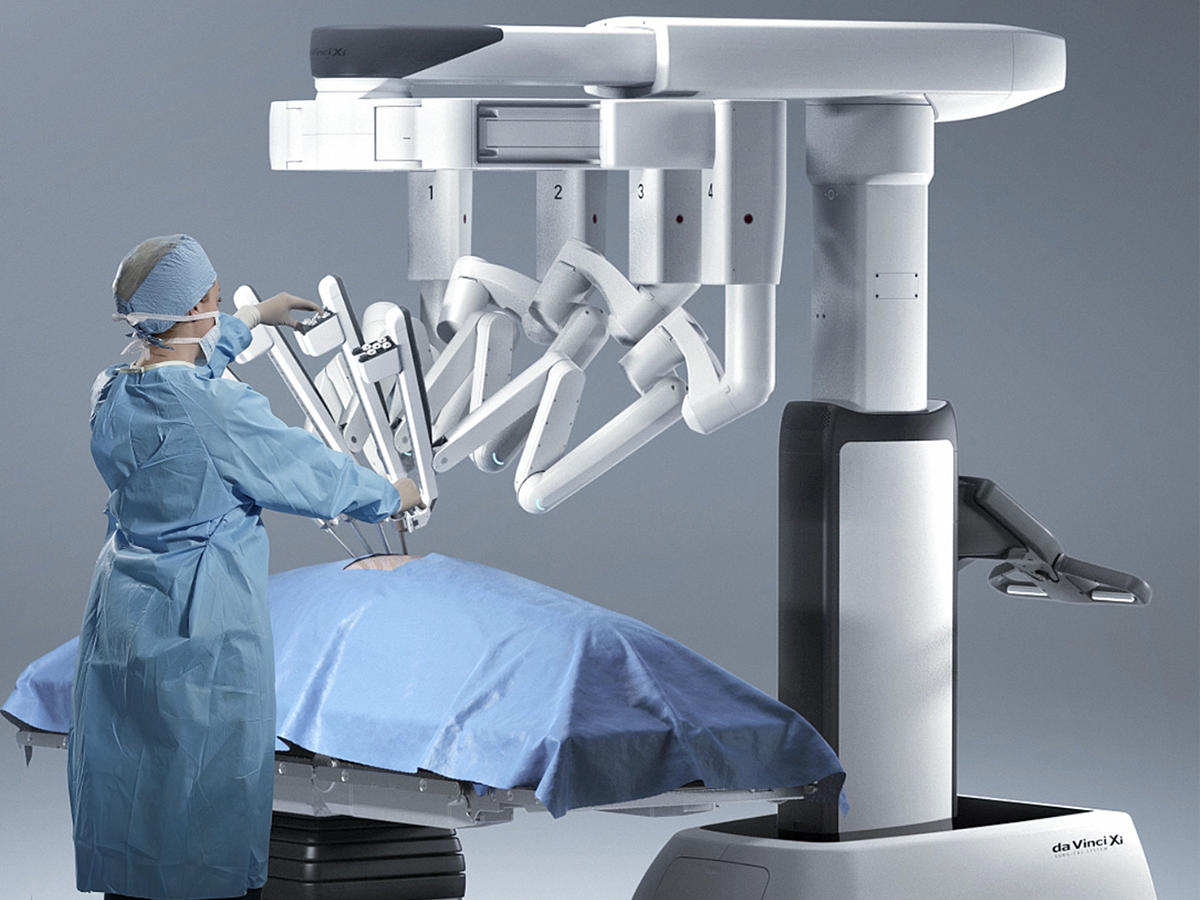
3. Computer Vision (CV): CV algorithms assess visual input from medical photos, videos, and sensors to assist in diagnosis, surgery planning, and monitoring. They segment organs, follow disease progression, and identify anomalies to enhance workflow accuracy and efficiency in the healthcare industry.
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP techniques infer information from unstructured text, such as electronic health records (EHRs), clinical notes, research articles, and patient interviews. They aid with clinical decision-making, information retrieval, and semantic understanding for applications such as automated coding, improved clinical recordkeeping, and literature reviews.
5. Robots and Automation: AI-driven robotics automate repetitive tasks, enhance rehabilitation and assistive care for patients with impairments or mobility limits, and support surgical procedures. They improve accuracy, reduce the chance of human error, and boost the capabilities of medical personnel.
6. Predictive Analytics and Population Health: AI systems analyze large data sets to identify trends, anticipate disease outbreaks, assess the risks to the general public’s health, and distribute resources as effectively as feasible. They promote proactive and data-driven healthcare delivery through their support of public health initiatives, chronic illness management, and preventative measures.
7. Virtual Health Assistants: AI is used by virtual agents, also known as chatbots, to communicate with patients, respond to questions, set up appointments, provide instructional materials, and remind patients to take their medications. In particular, they improve patient participation, ease of use, and accessibility in telehealth and remote monitoring situations.
AI’s advantages in healthcare
Better Clinical Outcomes: AI supports clinical decision-making by offering evidence-based recommendations, early disease identification, tailored treatment plans, and actionable insights. It improves patient outcomes across a range of medical specializations, lowers medical errors, and improves diagnostic accuracy.
Effective Workflows: AI minimizes paperwork for healthcare professionals, automates administrative duties, optimizes scheduling, and simplifies documentation. It increases the effectiveness of operations, lowers burnout, and frees up more time for interdisciplinary team collaboration and direct patient care.
Cost Savings: By optimizing resources, implementing preventative measures, lowering hospital readmission rates, and enhancing population health management, AI-driven systems can save healthcare expenses. They help healthcare firms find inefficiencies, cut waste, and improve revenue cycle management.
1.Improved Patient Experience: By offering individualized treatment plans, prompt treatments, remote monitoring choices, and self-service tools, artificial intelligence (AI) technologies improve patient involvement, communication, and satisfaction. They promote patient empowerment and loyalty by enhancing accessibility, convenience, and adherence to treatment plans.
2.Data-Driven Insights: From a variety of healthcare data sources, such as EHRs, medical imaging, genomics, wearables, and social determinants of health, AI algorithms produce useful insights. They encourage ongoing learning and innovation in the provision of healthcare by supporting population health analytics, clinical research, evidence-based medicine, and quality improvement programs.Obstacles and Things to Think AboutDespite the fact that AI has many advantages, there are some obstacles and factors to take into account before using it in healthcare:
a.Data Governance, Standardization, and Privacy Protection: As AI depends on objective, high-quality data for training and validation, these measures are essential. When implementing AI, concerns of data security, confidentiality, and compliance with laws like HIPAA must be carefully considered.
Algorithm Interpretability and Bias: AI algorithms may display biases as a result of training data, which could affect how decisions are made and how patients are treated. For healthcare AI frameworks to be ethical and to foster trust and responsibility, it is imperative that algorithmic fairness, transparency, and interpretability be guaranteed.
b.Integration and Interoperability: Smooth interoperability, compatibility, and usability are necessary for integrating AI solutions into current clinical settings, IT systems, and healthcare workflows. For successful deployment and acceptance, cooperative collaborations between healthcare providers, IT teams, and AI companies are vital.
c.Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: The application of AI in healthcare brings up a number of intricate issues pertaining to patient rights, algorithmic governance, responsibility, and accountability. For responsible AI implementation and risk minimization, compliance with industry standards, legal frameworks, and ethical principles is essential.
d.Workforce Readiness and Training: To properly use AI tools, evaluate algorithmic outputs, and incorporate AI into clinical practice, healthcare workers need to get training, education, and upskilling. To get the most out of AI investments in healthcare, interdisciplinary collaboration, constant learning, and data literacy must be fostered.
Methods of Performance
1. Needs assessment: Determine which operational, financial, and therapeutic problems AI can solve; rank use cases according to importance; establish success metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) for assessment.
2. Vendor Selection: Assess AI providers according to their experience, performance history, adherence to legal requirements, data security, interoperability, scalability, and congruence with the objectives and core values of the company.
3. Pilot Examining: AI solutions are validated, usability is evaluated, end users’ input is gathered, and iterations are made based on real-world insights and lessons acquired through pilot projects or proof-of-concepts.
4. Training and Education: Provide healthcare workers with comprehensive training, education, and support to familiarize them with AI tools, workflows, best practices, and ethical principles. 5.Change Management: By involving stakeholders, addressing concerns, encouraging buy-in, and assisting organizational change readiness, you can cultivate a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement.6. Performance Monitoring: Keep an eye on AI performance, user happiness, clinical results, ROI, and regulatory compliance at all times. Iterate in response to user feedback and data-driven insights.
In the future, a number of trends and advancements will influence how AI is used in healthcare:1. Multimodal Integration: To enable comprehensive patient profiles and tailored interventions, AI platforms will integrate a variety of data sources, such as medical imaging, genomics, real-time monitoring, patient histories, and social determinants. 2. Explainable AI: Technological developments in this area will improve the accountability, transparency, and interpretability of AI algorithms, allowing medical professionals to comprehend and rely on AI-driven recommendations and judgments. 3. AI Governance: Frameworks for AI governance will be established by healthcare organizations.